zkEVM
介绍
零知识虚拟机是一种生成零知识证明以验证VM智能合约程序运行正确性的虚拟机。本项目的虚拟机特指EVM,因此也用英文简写zkEVM指代零知识虚拟机。
zkEVM作为互联网3.0操作系统(ChainWeaver)中的重要部分,支撑EVM智能合约的可证明计算。zkEVM运行字节码并将其计算过程转换为特定格式,交给零知识证明电路并产生对应的零知识证明。zkEVM可以在layer 2扩容方案中作为生成有效性证明的核心部分,也可以在链网架构中作为信任增强工具增强链间信任。
本项目选择从EVM字节码层面进行兼容,因此原生可以支持Solidity、Vyper等智能合约语言。常用智能合约可以无成本地迁移至zkEVM,并使用相同的开发调试工具。
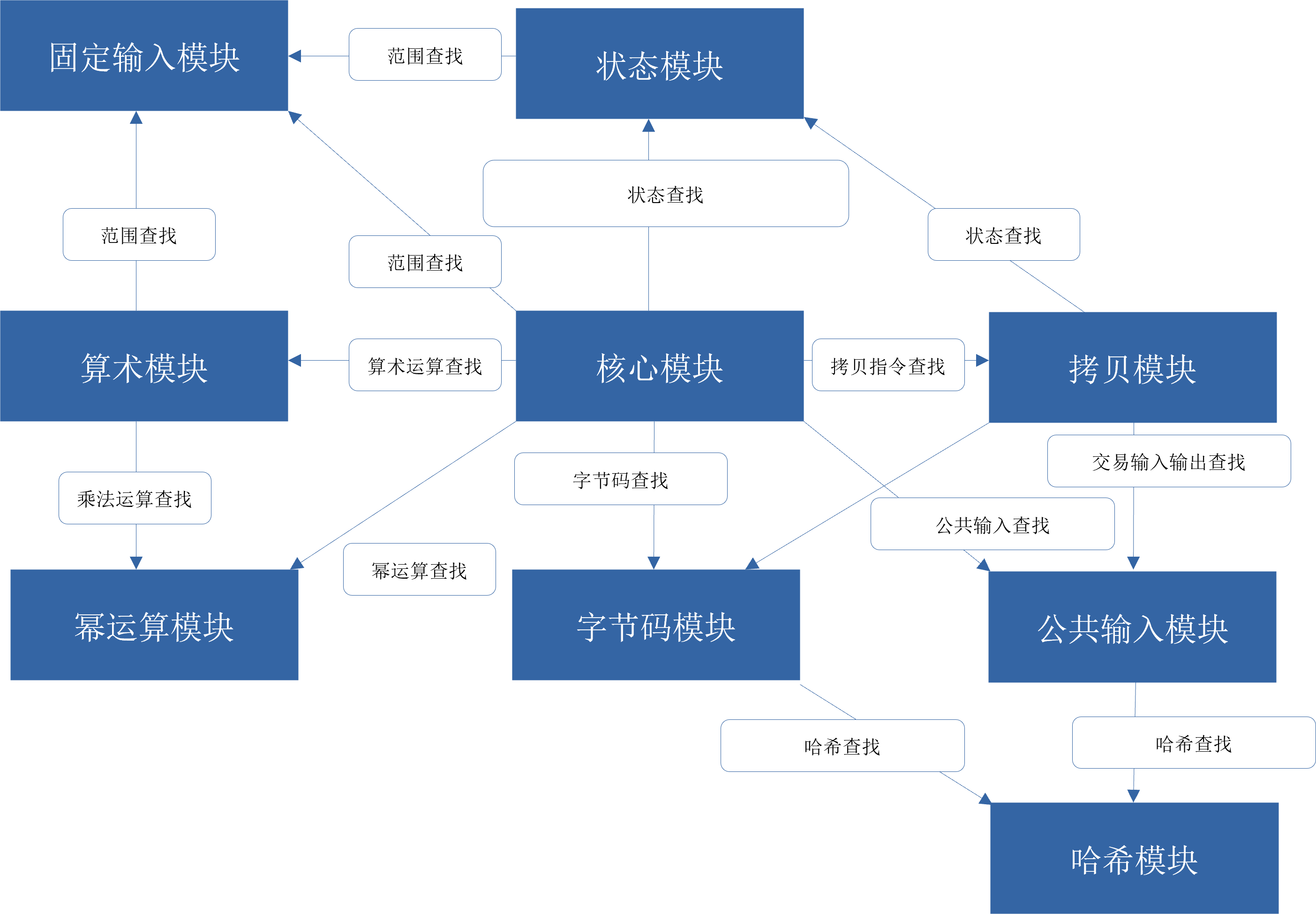
零知识证明电路包括两个核心要素,证据和约束。zkEVM中,证据由EVM内部的数据结构和执行过程经过特定格式转换而来,约束则检验数据结构和执行过程的正确性。构建证据和构建约束两者互相关联,互相影响,需要综合统筹。EVM的复杂性决定了电路的证据和约束将会非常复杂,进而决定了zkEVM的程序将会非常庞大。因此我们将zkEVM的电路程序开发进行逻辑上的拆分,由多个子电路分头进行处理,每个子电路可以构建自己的证据和约束。不同子电路所覆盖的逻辑基本不重叠,子电路间可通过“查找表”工具进行联系。这样,每个子电路需要考虑的情况就会简化,从而开发的难度也会显著减小。我们的设计包括如下子电路,
- 核心(Core),处理智能合约程序执行的每一步过程
- 状态(State),处理虚拟机中各类状态的读写
- 字节码(Bytecode),处理合约的字节码
- 拷贝(Copy),处理不定长数据的拷贝
- 固定输入(Fixed),处理运算中常见的固定输入
- 计算(Arithmetic),处理各类算数运算
- 公共输入(Public),处理合约的各种公共数据
- 幂运算(Exp),处理指数运算
- 哈希模块(keccak),处理哈希运算
出于对易用性和社区友好性的考虑,本项目选择halo2零知识证明电路开发框架及其算术化方法。
子电路
根据halo2的代码设计以及zkEVM的开发需要,定义了以下接口作为子电路的接口。上文所述的子电路(Core、State等等)均实现此接口,并通过接口并入最终的“超级电路(Super Circuit)”中。下面详细阐述其代码接口。
SubCircuitConfig
/// SubCircuit configuration
pub trait SubCircuitConfig<F: Field> {
/// Config constructor arguments
type ConfigArgs;
/// Type constructor
fn new(meta: &mut ConstraintSystem<F>, args: Self::ConfigArgs) -> Self;
}此接口包含new方法:新建column和建约束(即configure()的内容要在此方法里)。ConfigArgs是外界传进来的column,这些传进来的column就不必新建了。
那么,一个结构体MyConfig要实现此接口,一般其成员就要包括此子电路所使用的所有column。同时,此结构体一般还需要一些函数来帮助以后的分配数值(可选)。例如assign_row将具体数值填入所有column的一行。
SubCircuit
/// SubCircuit is a circuit that performs the verification of a specific part of
/// the full Ethereum block verification. The SubCircuit's interact with each
/// other via lookup tables and/or shared public inputs. This type must contain
/// all the inputs required to synthesize this circuit (and the contained
/// table(s) if any).
pub trait SubCircuit<F: Field> {
/// Configuration of the SubCircuit.
type Config: SubCircuitConfig<F>;
/// Cells that need to use permutation constraints.
type Cells;
/// Create a new SubCircuit from witness
fn new_from_witness(witness: &Witness) -> Self;
/// Returns the instance columns required for this circuit.
fn instance(&self) -> Vec<Vec<F>> {
vec![]
}
/// Assign only the columns used by this sub-circuit. This includes the
/// columns that belong to the exposed lookup table contained within, if
/// any; and excludes external tables that this sub-circuit does lookups
/// to. Return the cells that need to use permutation constraints.
fn synthesize_sub(
&self,
config: &Self::Config,
layouter: &mut impl Layouter<F>,
) -> Result<Self::Cells, Error>;
/// Number of rows before and after the actual witness that cannot be used, which decides that
/// the selector cannot be enabled
fn unusable_rows() -> (usize, usize);
/// Return the number of rows required to prove the witness.
/// Only include the rows in witness and necessary padding, do not include padding to 2^k.
fn num_rows(witness: &Witness) -> usize;
}此接口是为了负责EVM特定一部分的子电路而设计的。
-
type Config设置为上述的MyConfig。 -
Cells设置为要使用permutation约束的格子,目前为空()即可。 -
new_from_witness(witness: &Witness)创建一个新的子电路,输入是Witness,即证据,是一个包含所有电路输入的大表格。 -
instance返回此电路所需的公开列的具体数值。 -
synthesize_sub对此子电路进行synthesize操作,即分配值给子电路的格子。会返回Cells供permutation约束使用。 -
unusable_rows开始和最后不可用的行数,例如有约束要找前1行,那第一行就是不可用的,因为第一行再找前1行就找到错误的行数了。 -
num_rows统计一共要用多少行。
那么,一个结构体MyCircuit要实现此接口,一般其成员就包括一份Witness,其包括整张大表格,内含所有数值。需要注意的是,此结构体不包含MyConfig以及任何column,这是halo2的一种设计。
组合成为超级电路SuperCircuit
-
SuperCircuitConfig结构体包括所有子电路的config结构体 -
SuperCircuit结构体包括所有子电路的结构体 - 为
SuperCircuit实现halo2的Circuit接口,重点是两个方法:configure和synthesize。-
configure,即建立所需column和约束,只需依次调用子电路的构造函数new,然后将构造的所有子电路的config结构体组成SuperCircuitConfig返回。 -
synthesize,即分配值给子电路,只需依次调用子电路的方法synthesize_sub即可。
-
总结
- SubCircuitConfig的new,其包含了设置约束的configure功能。
- SubCircuit的synthesize_sub,其包含了分配值的synthesize功能。